股票上市市盈率一般是多少
Title: Understanding the PriceEarnings Ratio (P/E) for Unlisted Stocks
Introduction:
The priceearnings ratio (P/E ratio) is a commonly used valuation metric in the stock market. While it is often discussed in the context of listed companies, investors also consider the P/E ratio for unlisted or privately held stocks. In this article, we will explain what the P/E ratio is, how it is calculated, and discuss its relevance for unlisted stocks.
What is the P/E ratio?
The P/E ratio is a financial metric that measures the relative value of a company's stock based on its earnings. It is calculated by dividing the market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS). The P/E ratio indicates how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by the company.
Calculating the P/E ratio for unlisted stocks:
Since unlisted stocks do not have a readily available market price, calculating the P/E ratio is more challenging. In such cases, investors can estimate the market price by considering factors such as the company's intrinsic value, comparable valuations within the industry, and future growth prospects. The earnings per share can be obtained from the company's financial statements.
Understanding the P/E ratio for unlisted stocks:
The P/E ratio for unlisted stocks serves as a benchmark for comparing the company's valuation with its peers or industry standards. A higher P/E ratio suggests that investors expect higher future growth or have a positive outlook on the company, whereas a lower P/E ratio may indicate undervaluation or lower growth prospects.
Factors affecting the P/E ratio for unlisted stocks:
1. Industry dynamics: Different industries have varying growth rates and risk profiles, which influence the P/E ratios of unlisted stocks. For example, highgrowth industries like technology tend to have higher P/E ratios, while stable industries like utilities may have lower ratios.
2. Growth prospects: Companies with strong growth potential often command higher P/E ratios, as investors are willing to pay a premium for anticipated future earnings. Factors such as market share, competitive advantage, and innovation play a crucial role in determining growth prospects.
3. Risk factors: Unlisted stocks may carry higher risks compared to their listed counterparts, such as limited liquidity, lack of public information, and difficulty in exit options. These risks can impact the P/E ratio, potentially resulting in a discount compared to listed companies.
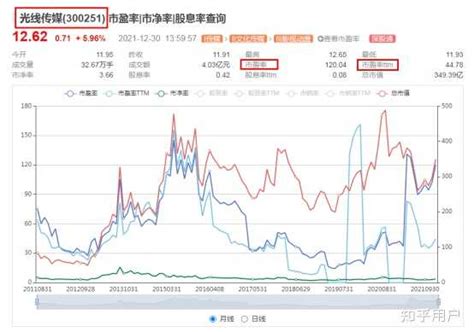
Using the P/E ratio for investment decisions:
1. Industry comparison: Compare the P/E ratio of the unlisted stock with other similar companies in the industry. If the stock's P/E ratio is significantly higher or lower, it is essential to understand the underlying reasons and assess the investment opportunity accordingly.
2. Growth expectations: Evaluate the company's growth prospects, future earnings potential, and the feasibility of achieving them. A higher P/E ratio may be justified if the company is expected to deliver aboveaverage growth.
3. Risk assessment: Consider the risks associated with investing in unlisted stocks, such as companyspecific factors, market volatility, and exit strategies. Balance the potential returns with the associated risks before making an investment decision.
Conclusion:
Although calculating and interpreting the P/E ratio for unlisted stocks requires additional analysis compared to listed stocks, it remains a valuable tool for evaluating and comparing the valuation of these companies. Investors should consider industry dynamics, growth prospects, and risk factors to make informed investment decisions. It is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence and seek professional advice when investing in unlisted stocks.
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户上传,若侵犯您权益,请联系我们,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052









